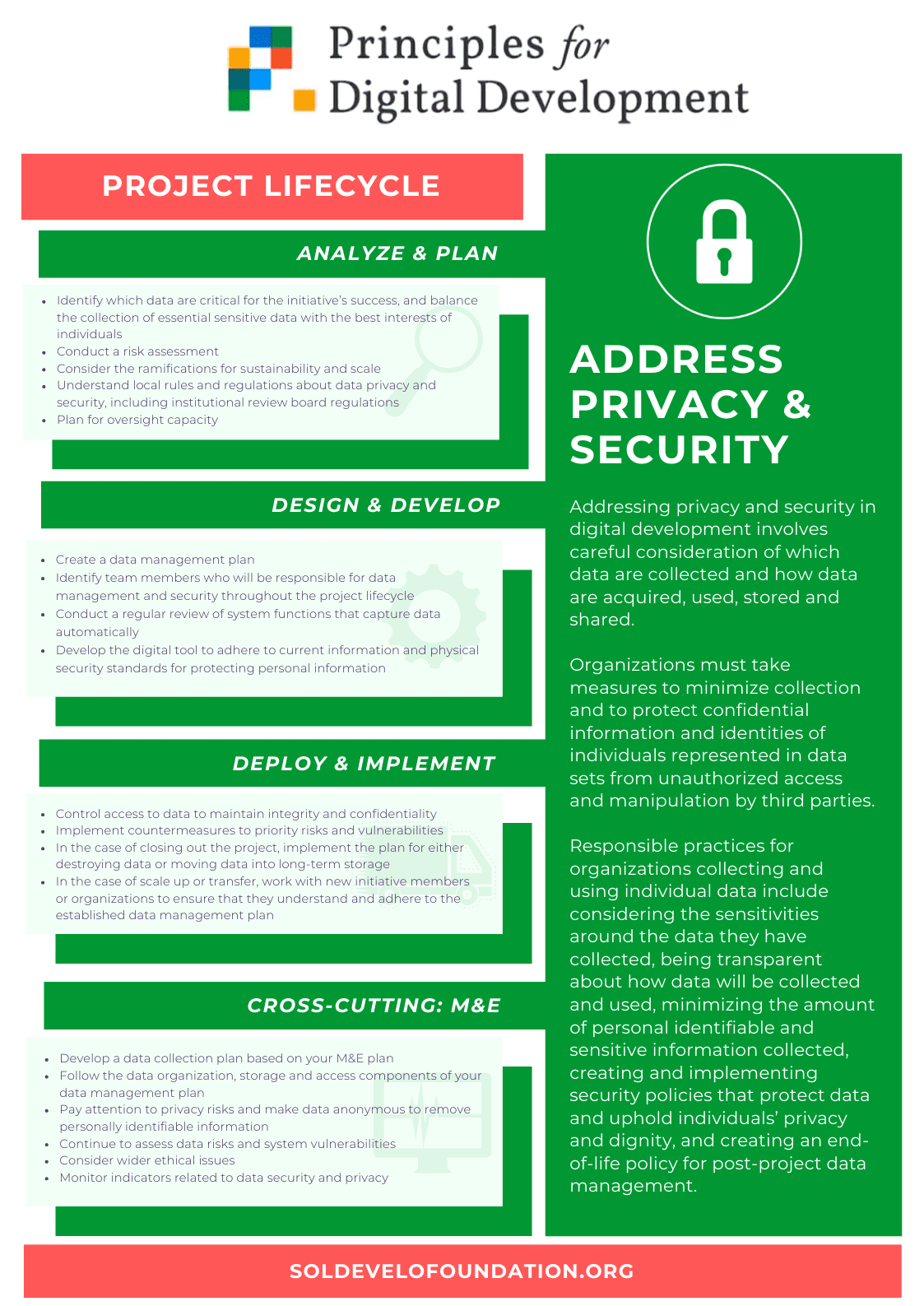
Address Privacy and Security is one of the most important topics of the 21st century where hackers and cyber hazard are at almost every corner. With only a few information they can steal your data, get into a bank account, steal emails and other sensitive information. To protect users in the real world and on the Internet, in 2018 the European Union has obliged member countries to follow new rules which are part of Directive (EU) 2016/680 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 April 2016. The statement is about the protection of individuals with regard to the processing of personal data. If your company is based in Europe this document should be the most important law for you. If you are based somewhere else you can also reuse and improve rules for your needs as we talked about it last week.
Under “address privacy and security” we mean taking care of collected data. How it is acquired, which data is gathered, where it is kept and for how long. Organizations should measure from which sources they collect the most data and trying to minimize statistics to protect yourself and its clients, partners, visitors etc. By creating and implementing security policies organizations protect data and avoid leakage of sensitive information.
First steps in creating privacy and security certificates
If you don’t know which steps you should consider in your plan we could help you. But remember that if you don’t feel ready to prepare security policies contact with some specialist. They will help you and secure you and your company from the legal side. Organizations which specialize in data protection, government officials, local leaders or your partners might help you. Also with a ready plan find out which open source programs are the best for you. Often companies like Microsoft, TechSoup may have some free programs for nonprofits.
Get to know local data protection laws, regulations and other statements which your company has to follow. Determine who gets to decide where to keep the data and for how long, who is allowed to use or transfer data and to what extent. Understand the penalties like fines, negative reputation as a consequence of noncompliance laws. Also, identify internal and external threats to your data, vulnerabilities, damages, number of stolen data and other dangers.
Identify which personal and user information is crucial to your organization and the success of projects. The less data you gather, the fewer problems and bureaucracy you have. Don’t keep data longer than you must. Try to minimize the amount of any sensitive data as much as you can.
Also, it’s important to inform others why their data are being collected, how data are used and shared. Participants (also employees) should be informed and understand their rights and obligations, risks and terms related to sharing their data. All information should be easy to understand for the local community. It means using the local language, unsophisticated vocabulary and ease of reading.
Be transparent and educate others about your good practics in security data. Show your engagement in data protection and build trust in your partners. Also, try to update your protection every time when it’s possible. Do it by adopting good solutions from others like two-factor authentication, encrypted files, secure servers or cloud storage. Don’t forget about contracts and data-sharing agreements with your partners, suppliers.
Data management plan
To make your work easier prepare documentation and training for all your staff which help learn and organize knowledge. After that, anybody won’t have doubts about the storage and usage of personal data. If you know any projects, where you will be obligated to track a huge amount of data, prepare a plan. Include spare offline storage like hard drives, pen drives, flash drives. Remember to delete or pass the data to authorized persons. So you can’t have access to data longer than your permission from the user.
A data management plan will help you during projects and organize a system to gather data. Each project is different and requires other information about participants so before start try to answer on a few questions:
- How much data will be collected? How long it will be collected and where will be stored, who is responsible for the collection, management and security? Do you need any help from outside?
(Being responsible include changes in the data management plan, monitoring data, secure and analyze threats, giving access and deleting data’s users.)
- What types of data includes a cleaning process? Are you obligated to delete all data or keep part of them after a project? How will you do this?
- Who has the rights to the data? How it will be shared (in what file format, how looks like procedure, passwords, authorization etc)? What type of documents do you need to secure all data and share information?
The Lifecycle of “Adress Privacy and Security”
Continue your journey with the Digital Principles and read about the 9th and the last one – “Be Collaborative“:
Learn to use Digital Principles in practice:
Digital Principles Organizational Self-Assessment
Digital Principles Indicator Library
Digital Principle-Focused Evaluation
The Principles For Digital Development: Gold Practices




